Abstract
Background
Pituitary surgical intervention remains the preferred treatment for Cushing’s disease (CD) while postoperative venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a significant risk. Whether to prescribe pharmacological thromboprophylaxis presents a clinical dilemma, balancing the benefit of reducing VTE risk with the potential for increasing hemorrhagic events in these patients. Currently, strong evidence and established protocols for routine pharmacological thromboprophylaxis in this population are lacking. Therefore, a randomized, controlled trial is warranted to determine the efficacy and safety of combined pharmacological and mechanical thromboprophylaxis in reducing postoperative VTE risk in patients with CD.
Methods
This investigator-initiated, multi-center, prospective, randomized, open-label trial with blinded outcome assessment aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combined pharmacological and mechanical thromboprophylaxis compared to mechanical thromboprophylaxis alone in postoperative patients with CD. A total of 206 patients diagnosed with CD who will be undergoing transsphenoidal surgery will be randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either combined pharmacological and mechanical thromboprophylaxis (intervention) or mechanical thromboprophylaxis only (control). The primary outcome is the risk of VTE within 12 weeks following surgery.
Discussion
This trial represents a significant milestone in evaluating the efficacy of combined pharmacological and mechanical prophylaxis in reducing VTE events in postoperative CD patients.
Trial registration
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04486859, first registered on 22 July 2020.
Administrative information
Note: the numbers in curly brackets in this protocol refer to SPIRIT checklist item numbers. The order of the items has been modified to group similar items (see http://www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/spirit-2013-statement-defining-standard-protocol-items-for-clinical-trials/).
| Title {1} | Postoperative Initiation of Thromboprophylaxis in patients with Cushing’s Disease (PIT-CD): a randomized control trial |
| Trial registration {2a and 2b} | ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04486859, first registered on 22 July 2020
WHO Trial Registration Data Set (Supplement) |
| Protocol version {3} | Date: 1 July 2021, Version 5.0 |
| Funding {4} | The trial is supported by Clinical Research Plan of SHDC (SHDC2020CR2004A). |
| Author details {5a} | Nidan Qiao, Min He, Zhao Ye, Wei Gong, Zengyi Ma, Yifei Yu, Zhenyu Wu, Lin Lu, Huijuan Zhu, Yong Yao, Zhihong Liao, Haijun Wang, Huiwen Tan, Bowen Cai, Yerong Yu, Ting Lei, Yan Yang, Changzhen Jiang, Xiaofang Yan, Yanying Guo, Yuan Chen, Hongying Ye, Yongfei Wang, Nicholas A. Tritos, Zhaoyun Zhang, Yao Zhao. |
| Name and contact information for the trial sponsor {5b} | Investigator initiated trial, principal investigators, post-production correspondence:
Yao Zhao (YZ), Department of Neurosurgery, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, 12 mid Wulumuqi Rd, Shanghai 200040, China. Email: zhaoyao@huashan.org.cn Zhaoyun Zhang (ZZ), Department of Endocrinology, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, 12 mid Wulumuqi Rd, Shanghai 200040, China. Email: zhangzhaoyun@fudan.edu.cn |
| Role of sponsor {5c} | The trial sponsor holds responsibility for all key elements of the trial’s execution, including its design, data collection, management, analysis, interpretation of results, and reporting. An independent Data Safety Monitoring Board monitors data safety and participant protection to ensure the trial’s integrity and the safety of participants. |
Introduction
Background and rationale {6a}
Cushing’s disease (CD) is characterized by hypercortisolism resulting from an adrenocorticotropic hormone-secreting pituitary adenoma [1]. Tumor-directed surgical intervention remains the preferred treatment for this condition. Patients with Cushing’s disease commonly experience a hypercoagulable state due to activation of the coagulation system [2], suppression of anticoagulation and fibrinolytic pathways, and enhanced platelet activation, significantly increasing their risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE). Postoperative VTE risk is further exacerbated by factors such as intravenous medications, blood loss, and prolonged bed rest. Multiple studies report postoperative VTE risks in patients with CD ranging from 3 to 20% [2,3,4,5].
The Endocrine Society and Pituitary Society recommends considering perioperative thromboprophylaxis as a strategy to reduce VTE risk in patients with CD [1, 6]. However, this recommendation was based on a single study that investigated perioperative prophylactic anticoagulation in patients with Cushing’s syndrome [7]. The study was limited by its small sample size, single-center nature, and retrospective design. Crucial details such as the optimal timing for initiation, choice of anticoagulant, and duration of therapy were not established. Recent surveys of European and US centers indicate that thromboprophylaxis protocols are not routinely employed, and there is considerable heterogeneity in prophylactic practices across centers [8, 9].
The primary risk associated with thromboprophylaxis is postoperative hemorrhage. In patients with CD, although the risk of bleeding is significantly lower than after a typical craniotomy, complications such as intrasellar hemorrhage and nasal bleeding may still occur. Due to its retrospective nature, the aforementioned study cannot conclusively determine whether the benefits of thromboprophylaxis outweigh its risks. Consequently, guidelines from hematology and neurosurgical societies have concluded that the current evidence is insufficient to support a standardized VTE prophylaxis regimen for neurosurgical patients [10,11,12]. Nevertheless, both the American Society of Hematology and European guidelines suggest that a combination of pharmacological and mechanical prophylaxis may be justified for higher-risk subgroups [10, 13].
Objectives {7}
Due to conflicting recommendations and lack of a definitive study to determine whether the benefits outweigh the risks regarding the use of pharmacological antithrombotic prophylaxis in patients with CD following pituitary surgery, we initiated this study, called Postoperative Initiation of Thromboprophylaxis in Patients with Cushing’s Disease (PIT-CD). The aim of this study is to evaluate whether the combined use of pharmacological and mechanical prophylaxis reduces VTE events compared to mechanical prophylaxis alone in postoperative CD patients.
Trial design {8}
Our hypothesis was that pharmacological prophylaxis in combination with intermittent pneumatic compression would be superior to intermittent pneumatic compression alone.
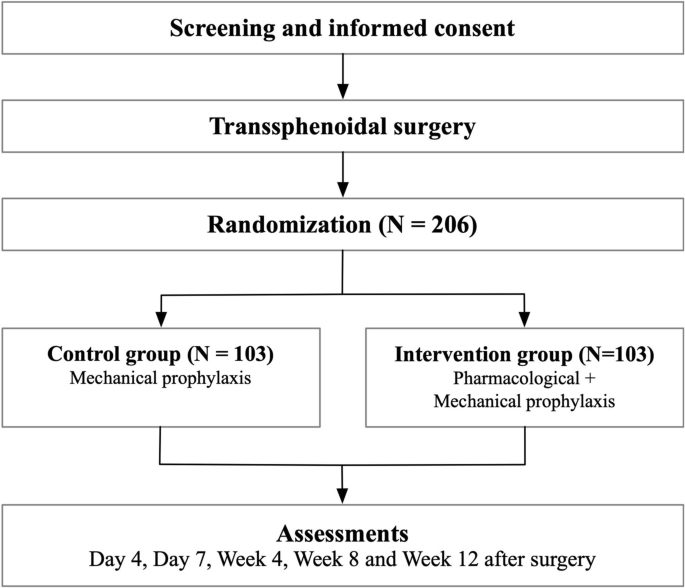
The PIT-CD study is an open-label, multicenter, prospective, randomized clinical trial with open-label treatment designed to assess the efficacy of combined pharmacological and mechanical prophylaxis compared to mechanical prophylaxis alone. Patients are randomized in a 1:1 ratio. The patient flow is illustrated in Fig. 1.
Methods: participants, interventions and outcomes
Study setting {9}
This study was initiated in tertiary centers across China with expertise in managing patients with CD. Currently, seven centers (see Supplements) are actively recruiting patients for the study.
Eligibility criteria {10}
Inclusion criteria
Patients are eligible for inclusion if they meet the following criteria:
- 1.Age between 18 and 65 years (inclusive)
- 2.Diagnosed with CD and scheduled to undergo transsphenoidal surgery
- 3.Either newly diagnosed or recurrent disease
A diagnosis of CD is confirmed based on the following criteria:
- A.Twenty-four-hour urine free cortisol > upper normal boundary and low-dose dexamethasone suppression test (overnight or over two days): serum cortisol > 1.8 µg/dL
- B.8 AM serum adrenocorticotropic hormone > 20 pg/mL
- C.High-dose dexamethasone suppression test: serum cortisol or 24-h urine cortisol suppression > 50%
- D.Inferior petrosal sinus sampling (IPSS) indicates elevated adrenocorticotropic hormone central gradient consistent with secretion from a central source
Patients are diagnosed with CD if both criteria A and B are met, in addition to either C or D. In patients with tumors smaller than 6 mm on MRI, IPSS indicating a central source is essential.
Exclusion criteria
Patients will be excluded from the study if they meet any of the following criteria:
- 1.History of VTE before surgery or within 24 h post-surgery
- 2.Acute bacterial endocarditis
- 3.Major bleeding events within the previous 6 months
- 4.Thrombocytopenia
- 5.Active gastrointestinal ulcers
- 6.History of stroke
- 7.High risk of bleeding due to clotting abnormalities
- 8.Participation in other clinical trials within the last three months
- 9.Contraindications to rivaroxaban (e.g., renal dysfunction with eGFR < 50 mL/min)
- 10.Presence of malignant diseases
- 11.Severe mental or neurological disorders
- 12.Presence of intracranial vascular abnormalities
- 13.Contraindications to mechanical prophylactic anticoagulation
- 14.Pregnancy
- 15.Any other condition that researchers deem inappropriate for study participation (e.g., oral contraceptive use, history of thrombophilia)
Who will obtain informed consent? {26a}
Patients with CD are provided with detailed information about the clinical trial, including known and foreseeable risks and potential adverse events. Investigators are required to thoroughly explain these details to the patients or their guardians if the patients lack capacity to provide consent. Following a comprehensive explanation and discussion, both the patients or their guardians and the investigators sign and date the informed consent form.
Additional consent provisions for collection and use of participant data and biological specimens {26b}
N/A. Biological specimens are unnecessary in this trial. Participant data was not intended to be included in any other ancillary studies.
Interventions
Explanation for the choice of comparators {6b}
Participants in the control arm of the study will be required to use a limb compression system twice daily, for 30 min each session, from the 2nd to the 7th day post-surgery. The intermittent pneumatic compression devices are the standard of care in the prevention deep vein thrombosis in many literatures [14, 15].
Intervention description {11a}
Participants in the intervention arm of the study will be required to use the same limb compression system, also for 30 min twice daily from the 2nd to the 7th day post-surgery. Additionally, participants will receive subcutaneous injections of low molecular weight heparin (4000 IU) once daily from the 2nd to the 4th day post-surgery. Starting on the 5th day and continuing through the 28th day post-surgery, participants will take oral rivaroxaban tablets (10 mg) once daily.
Criteria for discontinuing or modifying allocated interventions {11b}
Participants have the right to withdraw their consent at any time without providing a reason, thereby terminating their participation in the study. Any withdrawal and the reasons, if known, will be documented. Criteria for premature termination include the following: occurrence of the primary outcome (patients will still be monitored for safety for 12 weeks), failure to meet inclusion criteria, fulfillment of exclusion criteria, or loss of contact.
Strategies to improve adherence to interventions {11c}
Several strategies will be employed to maintain adherence to interventions in this trial. Participants will receive thorough preoperative education on the importance of pharmacological and mechanical prophylaxis in preventing VTE if they are assigned to the intervention arm or the importance of mechanical prophylaxis if they are assigned to the control arm. Detailed instructions on the use of the limb compression system and administration of rivaroxaban will be provided. Pill counts will be performed to document adherence in the intervention group.
Relevant concomitant care permitted or prohibited during the trial {11d}
N/A. Participants in both groups will receive treatment according to the current standard-of-care.
Provisions for post-trial care {30}
Participants experiencing adverse events will be followed until the events are resolved. Other participants will be regularly followed in accordance with clinical routine clinical practice. Participants in the trial are compensated in the event of trial-associated harms.
Outcomes {12}
Primary outcome
The primary outcome of the study is the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) within 12 weeks after surgery. VTE is defined as either deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE), regardless of whether the cases are symptomatic or asymptomatic.
Secondary outcomes
The secondary outcomes are as follows: (1) risk of DVT within 12 weeks after surgery; (2) risk of PE within 12 weeks after surgery; (3) risk of symptomatic DVT, symptomatic PE, or symptomatic VTE within 12 weeks after surgery; (4) risk of VTE-associated mortality within 12 weeks after surgery; (5) risk of all-cause mortality within 12 weeks after surgery.
“Symptomatic” is defined as the presence of one or more of the following symptoms attributed to VTE: pain or swelling in the affected leg; chest pain, dyspnea, or decreased oxygen saturation.
Safety outcomes
Safety outcomes include the following: (1) major bleeding; (2) minor bleeding; (3) hemorrhage-associated surgery; (4) hemorrhage-associated readmission; (5) coagulation disorders (APTT or INR > 2.5 normal upper boundary); (6) thrombocytopenia; (7) increase in liver function tests.
Major bleeding is defined according to the Subcommittee on Control of Anticoagulation of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis [16]. This includes fatal bleeding; bleeding that is symptomatic and occurs in a critical area or organ; extrasurgical site bleeding causing a fall in hemoglobin level of 20 g/L or more, or leading to transfusion of two or more units of whole blood or red cells; surgical site bleeding that requires a second intervention.
Participant timeline {13}
A schema of all trial procedures and clinical visits is summarized in Table 1.
Sample size {14}
Our estimates are based on a retrospective study examining the effects of preventive anticoagulation during the perioperative period in Cushing syndrome [7]. This study reported that the risk of postoperative VTE was lower in patients receiving preventive anticoagulants (6%) compared to those who did not (20%). Therefore, we assume that the risk of the primary outcome in the control group is 20%, while in the intervention group it is 5% within 12 weeks. Based on these assumptions, we calculated the required sample size for each group to be is 93 using PASS software, with an alpha level of 0.05 and a power of 0.9. Accounting for an estimated 10% dropout rate, the total number of patients required is 206.
Recruitment {15}
Clinical investigators will receive training on communicating with potential patients and their relatives, documenting screening logs, and other standard operating procedures during the kick-off meeting at each participating center. All centers will recruit patients competitively, and recruitment progress will be monitored to track the process. The estimated recruitment rate is 8 to 10 patients per month, with an expected recruitment period of 2 years.
Assignment of interventions: allocation
Sequence generation {16a}
The randomization procedure is computer- and web-based, and is stratified by age (≤ 35 years old vs. > 35 years old), sex (female vs. male) and disease duration (≤ 2 years vs. > 2 years).
Concealment mechanism {16b}
Participants are randomized using a web-based randomization system (edc.fudan.edu.cn). This system maintains allocation concealment by withholding the randomization code until screening is complete.
Implementation {16c}
Investigators will enroll participants, with the stratified block algorithms generating a random allocation sequence. Participant assignment through the randomization system is not subject to influence by the clinical investigators.
Assignment of interventions: blinding
Who will be blinded {17a}
This is an open-label trial, meaning that both the treating physicians and the participants are aware of the treatment allocation. However, a separate group of clinical outcome assessors (Clinical Event Committee, CEC), who are blinded to the treatment allocation, will determine the clinical outcomes. Similarly, lower limbs ultrasound and pulmonary computed tomography angiography (CTA) assessments will be adjudicated by an Independent Review Committee (IRC) that is blinded to the treatment allocation. Statisticians remain blinded to treatment allocation prior to the final analysis, and the interim analyses will be conducted by a separate team from the one undertaking the final analysis.
Procedure for unblinding if needed {17b}
N/A. The design is open label.
Data collection and management
Plans for assessment and collection of outcomes {18a}
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) will be assessed using bilateral lower limb ultrasound. Asymptomatic participants will undergo evaluation at prespecified intervals (day 4, day 7, week 4, and week 12 post-intervention), while symptomatic individuals will receive immediate imaging upon presentation of clinical manifestations such as unilateral or bilateral lower extremity edema or pain. Pulmonary embolism (PE) screening will be performed via pulmonary computed tomography angiography (CTA) at day 7 in asymptomatic cases, with expedited assessment triggered by acute symptoms (e.g., chest pain, dyspnea) or radiographic evidence of DVT detected during lower limb ultrasonography. These events will be adjudicated by an Independent Review Committee (IRC). A CEC will be convened to assess other outcomes.
Plans to promote participant retention and complete follow-up {18b}
The initial intervention for participants takes place during the patient’s inpatient stay, during which researchers will provide detailed information about the required procedures. Participants will undergo routine follow-up at 4 weeks and 12 weeks post-surgery, with VTE-related follow-up arranged during these routine visits. Transportation and examination expenses for follow-up visits are reimbursable.
Data of those who discontinue will also be documented.
Data management {19}
Data will be kept, both on paper and in electronic databases, for at least 5 years. Data will be entered by clinical investigators using electronic case report forms (eCRFs) on a web-based platform (http://crip-ec.shdc.org.cn). The investigators will be introduced to the platform and trained in data entry during the initial kick-off meeting before the recruitment of the first study participant. Access to the study database will be restricted to authorized clinical investigators, who will use a personal ID and password to gain entry.
Confidentiality {27}
When adding a new participant to the database, identifying data (e.g., Chinese name) are entered on a form that is printed but not saved on the server. On this form, participants will be represented by a unique ID. The printed form is kept in a locked space accessible only to the principal investigator and may be used to unblind personal data if necessary.
Plans for collection, laboratory evaluation and storage of biological specimens for genetic or molecular analysis in this trial/future use {33}
N/A. There will be no biological specimens collected.
Statistical methods
Statistical methods for primary and secondary outcomes {20a}
The primary analysis will be conducted on the full analysis data set, adhering to the intention-to-treat principle, which includes all patients randomized in the study. Generalized linear models (GLMs) with binomial distribution will be employed to analyze primary, secondary, and safety outcomes. Treatment effects for these outcomes will be quantified as risk differences (RDs) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Additionally, odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals will be calculated using a logistic regression model, and hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals will be calculated using a Cox Proportional model.
Safety analyses will be based on all randomized patients who have received the study treatment. The risk and percentages of adverse events (AEs) and serious adverse events (SAEs) will be summarized by treatment group. Instances of subject death will be summarized and listed. All analyses will be performed using the SAS system, version 9.4.
Interim analyses {21b}
The Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) plans to convene the interim analysis meeting after randomization and 12-week follow-up visits are completed for 103 participants. The significance level for interim analysis (primary outcome) is set at 0.001 according to the Haybittle–Peto boundary principle.
Based on these analyses, the DSMB will advise the steering committee on whether the randomized comparisons in this study have demonstrated a clear benefit of the intervention. If the p-values from the interim analysis for both groups are less than 0.001, recruitment will be halted, and the study will meet the criteria for early termination. If the p-values are greater than or equal to 0.001, recruitment will continue until the planned sample size is achieved, with the final analysis significance level set at 0.049.
Methods for additional analyses (e.g., subgroup analyses) {20b}
For both primary and secondary outcomes, pre-specified subgroup analyses will be conducted based on sex, age, disease duration, and magnitude of urine free cortisol elevation.
Methods in analysis to handle protocol non-adherence and any statistical methods to handle missing data {20c}
The primary analysis will be conducted on the intention-to-treat data set, which includes all randomized patients and is based on the treatment arm to which they were assigned, regardless of the therapy they actually received. A per-protocol analysis will also be performed to account for non-adherence. If appropriate, multiple imputation will be used to address any missing data in the dataset. The prespecified statistical analysis plan (SAP), developed by independent biostatisticians blinded to treatment allocation, will be prospectively registered on ClinicalTrials.gov prior to database lock.
Plans to give access to the full protocol, participant-level data and statistical code {31c}
The trial was prospectively registered in ClinicalTrials.gov with the Identifier NCT04486859. Updates to reflect significant protocol amendments will be submitted. The statistical analysis protocol will also be updated prior to database locking. The datasets and statistical code are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Oversight and monitoring
Composition of the coordinating centre and trial steering committee {5d}
The trial steering committee is composed of four Chinese experts and two international experts from outside of China. Investigators in participating centers are required to attend a training course during a kick-off event organized by the principal investigator. Each investigator must confirm that they have been properly introduced to trial-specific procedures. An IRC will adjudicate primary outcomes. An independent CEC will be responsible for ensuring high-quality outcomes and minimizing inconsistencies or bias in the clinical trial data.
Composition of the data monitoring committee, its role and reporting structure {21a}
The Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) consists of three members, including one statistician. The DSMB will regularly receive blinded statistical reports and monitor serious adverse events throughout the trial to assess patient safety and determine if the trial should be terminated prematurely due to safety concerns.
An initial DSMB meeting will be conducted to ensure that DSMB members fully understand the research protocol, review and approve the DSMB charter, assess the monitoring plans for safety and efficacy data, and discuss the statistical methods, including stopping rules. A second DSMB meeting will be conducted to review the interim analysis. The interim analyses and the treatment allocation data will be provided by an independent trial statistician and provided confidentially to the DSMB chairman. An ad hoc DSMB meeting may be convened by either the principal investigators or the DSMB if imminent safety issues arise during the trial.
Adverse event reporting and harms {22}
Adverse events (AEs) and serious adverse events (SAEs) are defined according to the ICH GCP guidelines. All AEs and SAEs reported by study participants or observed by investigators within the study period must be documented in the eCRF and reported to the DSMB. Additionally, SAEs must be reported to the IRB.
Anticipated adverse events, including both major and minor bleeding events (e.g., epistaxis necessitating readmission), as well as coagulation disorders, thrombocytopenia, and elevated liver function tests, will be prospectively monitored in all trial participants. Unanticipated adverse events (not pre-specified in Section {12}) will be captured through spontaneous reporting. All adverse event data will be classified and graded according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0 to ensure consistency. For reporting, we will disclose all protocol-specified adverse events from Section {12}, alongside any unanticipated events higher than Grade 3.
Frequency and plans for auditing the trial conduct {23}
The trial conduct will be regularly audited to ensure compliance with the study protocol and Good Clinical Practice guidelines. Audits will be conducted by independent monitors from Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Developing Centers. These audits will involve reviewing study documentation, informed consent forms, source data verification, and adherence to the protocol. Audits will also assess data entry accuracy and the overall management of the trial. The frequency of these audits will be determined based on the recruitment rate, safety concerns, and previous audit findings.
Plans for communicating important protocol amendments to relevant parties (e.g., trial participants, ethical committees) {25}
Any modifications to the study protocol will require protocol amendments, which will be promptly submitted for approval to the Institutional Review Board. These changes will only be implemented after receiving approval from the Institutional Review Board. Once approved, ClinicalTrials.gov will be updated to reflect any significant changes. If necessary, protocol training to implement the amendments will be provided by the study team to participating centers.
Dissemination plans {31a}
After database closure and data analysis, the trial statistician will prepare a report detailing the main study results. Following this, a meeting of the investigators will be convened to discuss the findings before drafting a scientific manuscript for peer review and publication in a major scientific journal. Additionally, efforts will be made to present the results at key international conferences of neuroendocrine societies.
Discussion
This trial represents a significant milestone in evaluating the efficacy of combined pharmacological and mechanical prophylaxis in reducing VTE events in postoperative CD patients. To date, no similar randomized controlled trials have addressed this specific clinical question.
Transnasal transsphenoidal pituitary tumor resection is the preferred surgical approach for patients with CD. Compared to craniotomy, transsphenoidal surgery has a significantly lower risk of bleeding. The published literature indicates a bleeding risk of 0.02% following transsphenoidal surgery [17], whereas the incidence of intracranial hemorrhage after craniotomy ranges from 1% to 1.5% [18]. Therefore, for clinical practicality and safety, this study will exclusively include patients undergoing transsphenoidal resection.
Early meta-analyses indicated that low molecular weight heparin is generally safer, with a relatively lower bleeding risk compared to rivaroxaban, particularly when used for thrombosis prevention after hip and knee replacement surgeries [19]. However, recent studies have shown that rivaroxaban may have no significant difference in major bleeding and non-major bleeding risks compared to enoxaparin in thromboprophylaxis following non-major orthopedic surgeries of the lower limbs [20]. Given the risk of postoperative bleeding and the potential bleeding side effects of oral medications, LMWH was chosen for initial postoperative treatment because of its relatively lower bleeding risk. As patients prepare for discharge, the more convenient oral medication was selected for ongoing prophylaxis.
Patients who develop early VTE on the first day after surgery or despite anticoagulant use will be included in a further post hoc analysis. This will help identify risk factors for VTE. This analysis will aim to determine why VTE occurred despite anticoagulant use and explore whether specific factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, body mass index, or disease duration, are associated with increased risk. Based on our findings, recommendations may include earlier initiation of prophylaxis, dosage adjustments, or extended duration of treatment for high-risk patients.
Trial status
This protocol is based on trial protocol version 5.0, dated July 1, 2021. The first patient was enrolled in December 2020, and the final patient is expected to be enrolled by the end of 2024. While the original plan anticipated completing recruitment by December 2022, the COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted many districts and cities in China, leading to lockdowns that have severely delayed the implementation and recruitment for this trial.
Data availability {29}
Data will be made available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CD:
- Cushing’s disease
- VTE:
- Venous thromboembolism
- DVT:
- Deep vein thrombosis
- PE:
- Pulmonary embolism
- CEC:
- Clinical events committee
- IRC:
- Independent Review Committee
- CTA:
- Computed tomography angiography
- eCRFs:
- Electronic case report forms
- AE:
- Adverse events
- SAE:
- Severe adverse events
- DSMB:
- Data Safety Monitoring Board
References
-
Fleseriu M, Auchus R, Bancos I, Ben-Shlomo A, Bertherat J, Biermasz NR, et al. Consensus on diagnosis and management of Cushing’s disease: a guideline update. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(12):847–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00235-7.
-
Feelders RA, Nieman LK. Hypercoagulability in Cushing’s syndrome: incidence, pathogenesis and need for thromboprophylaxis protocols. Pituitary. 2022;25(5):746–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-022-01261-9.
-
White AJ, Almeida JP, Filho LM, Oyem P, Obiri-Yeboah D, Yogi-Morren D, et al. Venous Thromboembolism and Prevention Strategies in Patients with Cushing’s Disease: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2024;S1878–8750(24):01460–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2024.08.090.
-
Waqar M, Chadwick A, Kersey J, Horner D, Kearney T, Karabatsou K, et al. Venous thromboembolism chemical prophylaxis after endoscopic trans-sphenoidal pituitary surgery. Pituitary. 2022;25(2):267–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-021-01195-8.
-
Wagner J, Langlois F, Lim DST, McCartney S, Fleseriu M. Hypercoagulability and Risk of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Endogenous Cushing’s Syndrome: A Systematic Meta-Analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;9:805. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00805.
-
Nieman LK, Biller BM, Findling JW, Murad MH, Newell-Price J, Savage MO, et al. Treatment of Cushing’s Syndrome: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(8):2807–31. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-1818.
-
Boscaro M, Sonino N, Scarda A, Barzon L, Fallo F, Sartori MT, et al. Anticoagulant prophylaxis markedly reduces thromboembolic complications in Cushing’s syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(8):3662–6. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.87.8.8703.
-
White AJ, Almeida JP, Petitt JC, Yogi-Morren D, Recinos PF, Kshettry VR. Significant Variability in Postoperative Thromboprophylaxis in Cushing’s Disease Patients: A Survey of the North American Skull Base Society and the AANS/CNS Joint Tumor Section. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2023;85(5):540–5. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-1772698.
-
Isand K, Feelders R, Brue T, Toth M, Deutschbein T, Reincke M, et al. High prevalence of venous thrombotic events in Cushing’s syndrome: data from ERCUSYN and details in relation to surgery. Eur J Endocrinol. 2024;190(1):75–85. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejendo/lvad176.
-
Anderson DR, Morgano GP, Bennett C, Dentali F, Francis CW, Garcia DA, et al. American Society of Hematology 2019 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: prevention of venous thromboembolism in surgical hospitalized patients. Blood Adv. 2019;3(23):3898–944. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000975.
-
Nyquist P, Bautista C, Jichici D, Burns J, Chhangani S, DeFilippis M, et al. Prophylaxis of Venous Thrombosis in Neurocritical Care Patients: An Evidence-Based Guideline: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society. Neurocrit Care. 2016;24(1):47–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-015-0221-y.
-
Raksin PB, Harrop JS, Anderson PA, Arnold PM, Chi JH, Dailey AT, et al. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines on the Evaluation and Treatment of Patients With Thoracolumbar Spine Trauma: Prophylaxis and Treatment of Thromboembolic Events. Neurosurgery. 2019;84(1):E39–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyy367.
From https://trialsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13063-025-08923-6
Filed under: Cushing's, pituitary, Treatments | Tagged: Cushing's Disease, pituitary, post-op, thromboprophylaxis |



Leave a comment