Discussion
Epidemiology and clinical significance
CD is a severe endocrine disorder characterized by chronic exposure to excess glucocorticoids. Patients with CD have a two- to fivefold higher mortality compared with the general population, predominantly due to cardiovascular complications [4]. Chronic hypercortisolism is associated with systemic hypertension, left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), diastolic dysfunction, and accelerated atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of myocardial ischemia and heart failure. While these cardiovascular manifestations are common, the development of isolated dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) in the absence of other major comorbidities is rare but clinically noteworthy [9].
Pathophysiology of cardiac involvement
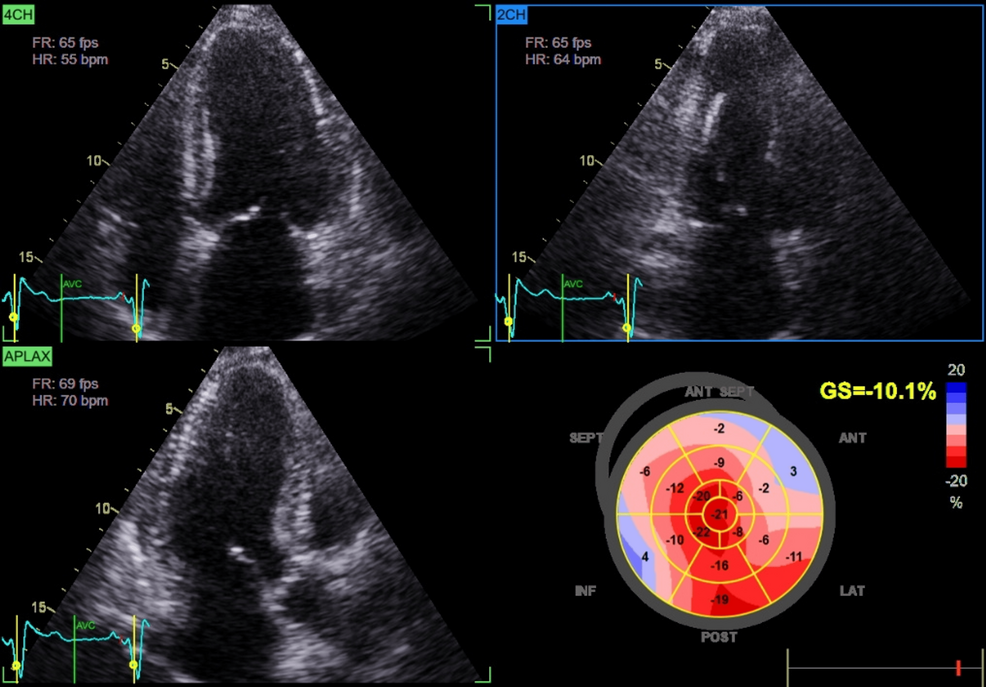
Chronic glucocorticoid excess contributes to cardiovascular remodeling via multiple mechanisms. Persistent hypertension and metabolic disturbances promote LVH and diastolic dysfunction. Additionally, glucocorticoid excess induces endothelial dysfunction, insulin resistance, and myocardial fibrosis, impairing ventricular compliance and predisposing to HFpEF [1,6]. Advanced echocardiographic techniques, such as GLS, can detect subclinical systolic dysfunction before overt reductions in LVEF [6]. In our patient, preserved LVEF (60%) coupled with markedly reduced GLS (-10%) and concentric LVH was consistent with HFpEF secondary to chronic cortisol excess, further supported by clinical signs of volume overload such as edema and severe hypertension [7].
Apical sparing and mimicking amyloidosis
An important observation in this case was relative apical sparing despite markedly reduced GLS, a strain pattern classically associated with cardiac amyloidosis [10]. Although infiltrative disease was excluded (negative serum and urine protein electrophoresis with immunofixation), this overlap illustrates how hypercortisolism-induced remodeling can phenocopy amyloidosis on imaging. Recent work has shown that hypercortisolism, beyond metabolic derangements, impairs myocardial mechanics and contractile efficiency [11]. Thus, patients with atypical strain findings should undergo careful endocrine evaluation to avoid misdiagnosis. Ultimately, the recognition that hypercortisolism may produce amyloid-like echocardiographic signatures has both diagnostic and management implications. It broadens the differential diagnosis of HFpEF and stresses the need for a multidisciplinary approach involving endocrinology and cardiology to prevent misdiagnosis and ensure tailored therapy.
Dilated cardiomyopathy in CS
Although uncommon, DCM with severe LV systolic dysfunction has been described in CS. Frustaci et al. reported eight cases of hypercortisolism due to adrenal adenoma among 473 patients with DCM (1.7%), all presenting with LVEF <30% and symptomatic heart failure. Endomyocardial biopsy revealed cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, interstitial fibrosis, and myofibrillolysis, distinct from idiopathic DCM and valvular disease controls. Follow-up biopsies in three patients one year post-adrenalectomy demonstrated substantial regression of these changes, highlighting the reversibility of glucocorticoid-induced myocardial injury [12].
Although not assessed in our patient, prior studies have implicated atrogin-1 in CS-related myocardial remodeling. At the molecular level, upregulation of atrogin-1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase expressed in skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle, was observed in CS-associated DCM compared with idiopathic DCM and controls [13]. Atrogin-1, implicated in skeletal muscle atrophy and sarcopenia, facilitates proteasomal degradation of intracellular proteins. Its overexpression in cardiomyocytes contributes to glucocorticoid-mediated myocardial remodeling. Importantly, atrogin-1 expression declined significantly following surgical correction of cortisol excess, paralleling improvements in cardiac structure and function. This reversibility mirrors recovery seen in glucocorticoid-induced skeletal myopathy and underscores the unique potential for cardiac recovery in CS-related DCM [9].
Clinical implications and differential diagnosis
This case underscores the multisystem burden of endogenous hypercortisolism, with particular cardiovascular susceptibility [1,6]. Chronic cortisol excess should be considered in the differential diagnosis of HFpEF, particularly when conventional risk factors coexist with systemic features such as central obesity, moon facies, and proximal myopathy [8]. Secondary causes of HFpEF, including cardiac amyloidosis, were excluded, supporting hypercortisolism as the primary etiology. Recognizing CS as a reversible contributor to myocardial dysfunction has important clinical implications, as timely endocrine intervention can improve cardiac function, lower blood pressure, and potentially prevent progression to irreversible myocardial remodeling.
Left ventricular hypertrophy and structural remodeling
Electrocardiographic and echocardiographic studies have characterized the cardiac phenotype in patients with CS. In a cohort of 12 consecutive patients, most had concomitant hypertension (11/12) and diabetes mellitus (7/12). Preoperative ECGs commonly demonstrated high-voltage QRS complexes (10 patients) and T-wave inversions (7 patients), indicative of LV strain. Echocardiography revealed LVH in nine patients, all exhibiting asymmetric septal hypertrophy. Interventricular septal thickness ranged from 16 to 32 mm, with septal-to-posterior wall ratios from 1.33 to 2.67. Compared with essential hypertension or primary aldosteronism, CS patients exhibited more pronounced LVH and a higher prevalence of asymmetric septal hypertrophy, suggesting a unique glucocorticoid-mediated remodeling pattern [13].
Postoperative follow-up in nine patients demonstrated normalization of ECG abnormalities, decreased septal thickness, and resolution of asymmetric septal hypertrophy in all but one patient, highlighting the partial reversibility of LVH following correction of hypercortisolism. The pronounced septal thickening relative to the posterior wall implies that excessive cortisol exposure, beyond hemodynamic effects of hypertension, contributes significantly to myocardial remodeling [13].
Impact of disease duration on concentric remodeling
Fallo et al. evaluated 18 patients with CS compared with 18 matched controls, adjusting for sex, age, body size, blood pressure, and duration of hypertension. Eleven participants in each group were hypertensive. Echocardiography revealed elevated relative wall thickness (RWT >0.45) in 11 patients with CS (five normotensive, six hypertensive) versus two hypertensive controls. Left ventricular mass index was abnormal in three CS patients and in four hypertensive controls, while systolic function was preserved in all participants [14].
No correlation was observed between RWT and either blood pressure or urinary cortisol levels in patients with CS. Instead, RWT correlated significantly with disease duration, indicating that prolonged exposure to glucocorticoid excess, rather than hormone levels or hemodynamic load, is the primary determinant of concentric LV remodeling. Postoperative echocardiography showed normalization of RWT in five of six patients previously affected, reinforcing the concept of reversible myocardial structural changes following correction of hypercortisolism [14].
Conclusions
CS represents a rare but clinically important etiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and, less commonly, dilated cardiomyopathy. Chronic hypercortisolism promotes systemic hypertension, LVH, diastolic dysfunction, myocardial fibrosis, and remodeling that may mimic infiltrative cardiomyopathies such as amyloidosis on echocardiography. GLS with apical sparing, although typically associated with amyloidosis, may also occur in cortisol-induced cardiomyopathy. Advanced imaging, including GLS, can detect subclinical myocardial impairment before overt systolic dysfunction develops. Notably, cardiac structural and functional abnormalities may partially or completely reverse following normalization of cortisol levels, highlighting the importance of early recognition and timely endocrine intervention. Clinicians should maintain a high index of suspicion for hypercortisolism in patients presenting with unexplained LVH, HFpEF, or atypical DCM, particularly when systemic features of CS are present. Future studies are needed to better characterize strain patterns in endocrine cardiomyopathies and to refine imaging-based algorithms for early detection.