In March of 1987, after the endo finally confirmed that I had Cushing’s, I was sent to a local hospital where they repeated all those same tests for another week and decided that it was not my adrenal gland (Cushing’s Syndrome) creating the problem. The doctors and nurses had no idea what to do with me, so they put me on the brain cancer ward.
When I left this hospital after a week, we didn’t know any more than we had before.
As luck would have it, NIH (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland) was doing a clinical trial of Cushing’s. I live in the same area as NIH so it was not too inconvenient but very scary at first to think of being tested there. At that time I only had a choice of NIH, Mayo Clinic and a place in Quebec to do this then-rare pituitary surgery called a Transsphenoidal Resection.
My husband asked my endo if it were his wife, if he would recommend this surgery. The endo responded that he was divorcing his wife – he didn’t care what happened to her. Oh, my!
I chose NIH – closest and free. After I was interviewed by the doctors there, I got a letter that I had been accepted into the clinical trial.
The night before I was admitted, I signed my will. I was sure I was going to die there. If not during testing, as a result of surgery.
The first time I was there was for 6 weeks as an inpatient. More of the same tests.
There were about 12 of us there and it was nice not to be alone with this mystery disease. Many of these Cushies (mostly women) were getting bald, couldn’t walk, having strokes, had diabetes. One was blind, one had a heart attack while I was there. Several were from Greece.
My first roommate was a nurse. She spent the entire first night screaming in pain. I was very glad when they moved me to a new room!
Towards the end of my testing period, I was looking forward to the surgery just to get this whole mess over with – either a cure or dying. While I was at NIH, I was gaining about a pound a day!
During the time I was home the weekend before surgery, a college classmate of mine (I didn’t know her) DID die at NIH of a Cushing’s-related problem. I’m so glad I didn’t find out until reading the alumnae magazine a couple months later! She was the same class, same major, same home-town, same disease…
We have a Scottish doctor named James Lind to thank for the clinical trial. He conducted the first ever clinical trial in 1747 and developed the theory that citrus fruits cured scurvy. Lind compared the effects of various different acidic substances, ranging from vinegar to cider, on groups of afflicted sailors, and found that the group who were given oranges and lemons had largely recovered from scurvy after 6 days.
I’d like to think that I advanced the knowledge of Cushing’s at least a little bit by being a guinea pig in 1987-1989.
From the NIH: http://endocrine.niddk.nih.gov/pubs/cushings/cushings.aspx
Hope through Research
Several components of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) conduct and support research on Cushing’s syndrome and other disorders of the endocrine system, including the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the National Cancer Institute, and the National Center for Research Resources.
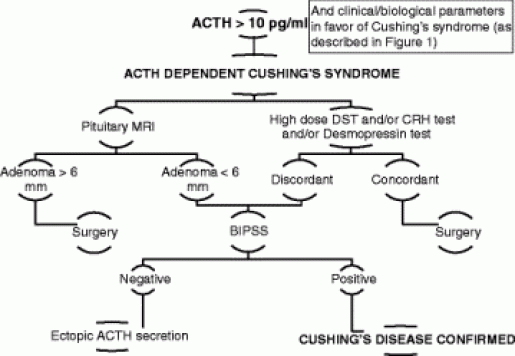
NIH-supported scientists are conducting intensive research into the normal and abnormal function of the major endocrine glands and the many hormones of the endocrine system. Researchers continue to study the effects of excess cortisol, including its effect on brain structure and function. To refine the diagnostic process, studies are under way to assess the accuracy of existing screening tests and the effectiveness of new imaging techniques to evaluate patients with ectopic ACTH syndrome. Researchers are also investigating jugular vein sampling as a less invasive alternative to petrosal sinus sampling. Research into treatment options includes study of a new drug to treat the symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome caused by ectopic ACTH secretion.
Studies are under way to understand the causes of benign endocrine tumor formation, such as those that cause most cases of Cushing’s syndrome. In a few pituitary adenomas, specific gene defects have been identified and may provide important clues to understanding tumor formation. Endocrine factors may also play a role. Increasing evidence suggests that tumor formation is a multistep process. Understanding the basis of Cushing’s syndrome will yield new approaches to therapy.
The NIH supports research related to Cushing’s syndrome at medical centers throughout the United States. Scientists are also treating patients with Cushing’s syndrome at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, MD. Physicians who are interested in referring an adult patient may contact Lynnette Nieman, M.D., at NICHD, 10 Center Drive, Room 1-3140, Bethesda, MD 20892-1109, or by phone at 301-496-8935. Physicians interested in referring a child or adolescent may contact Constantine Stratakis, M.D., D.Sc., at NICHD, 10 Center Drive, Room 1-3330, Bethesda, MD 20892-1103, or by phone at 301-402-1998.
Filed under: Clinical trials, Cushing's | Tagged: ACTH, brain cancer, Cancer, clinical trial, cortisol, Cushing's Awareness Challenge 2016, Dr. Constantine Stratakis, Dr. James Lind, Dr. Lynnette Nieman, MaryO, NIH, pituitary, surgery, transsphenoidal | 1 Comment »