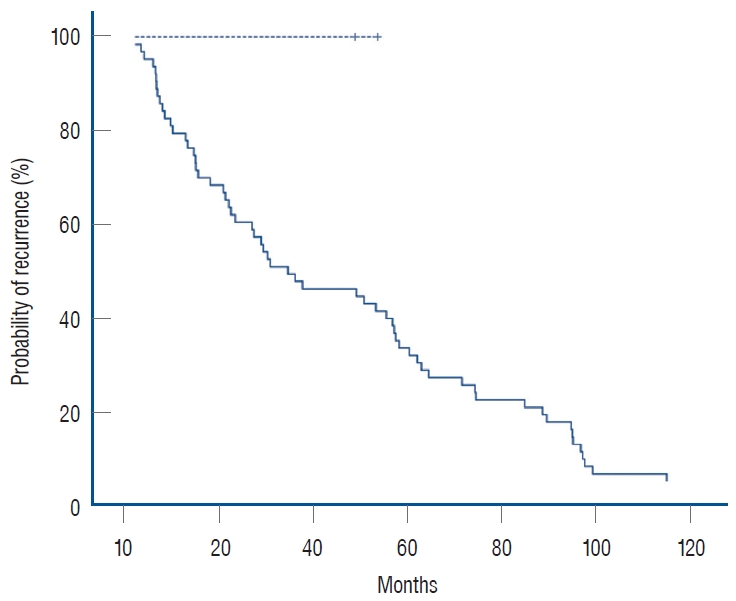
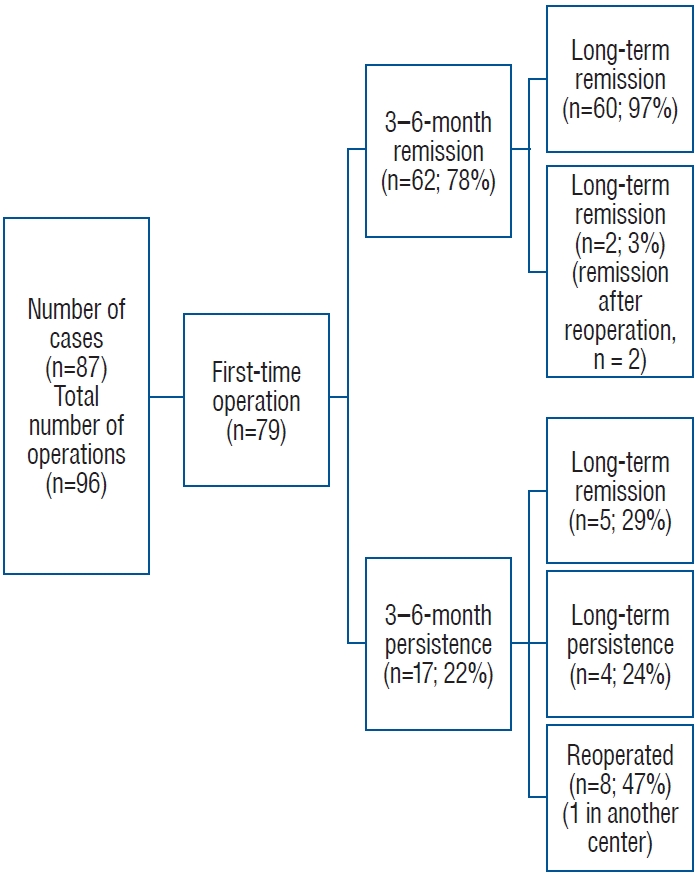
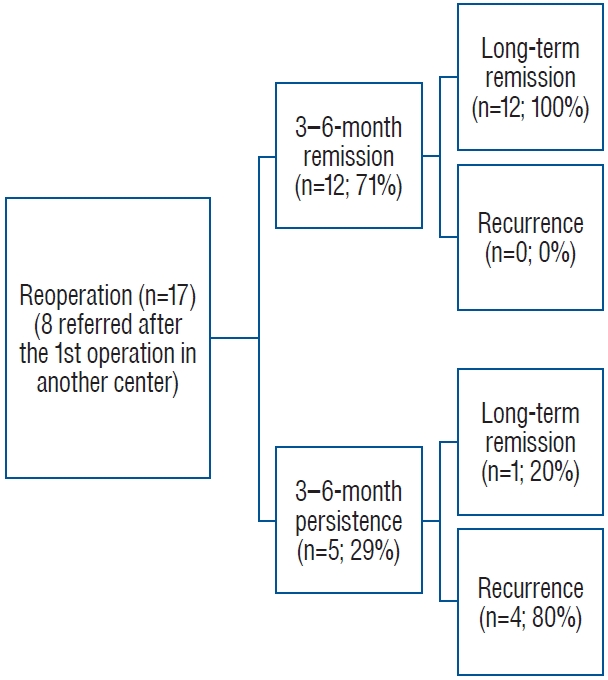
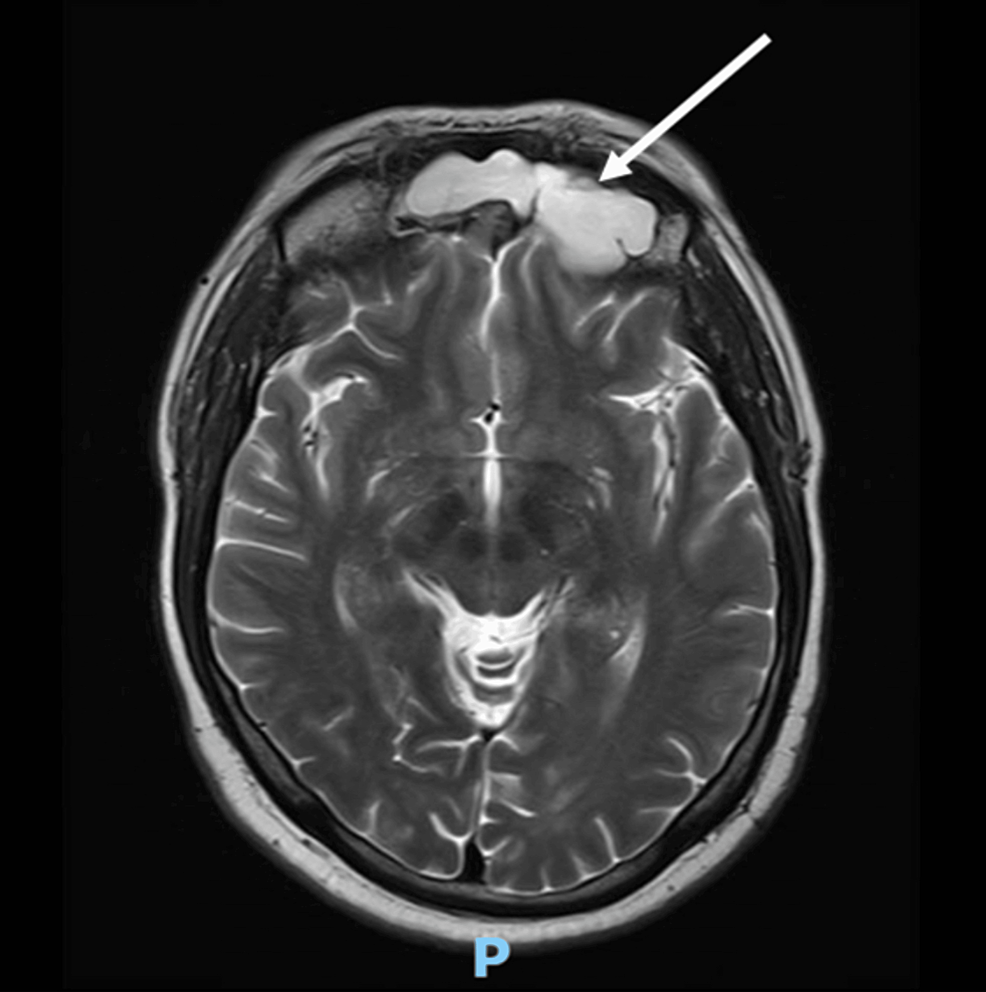
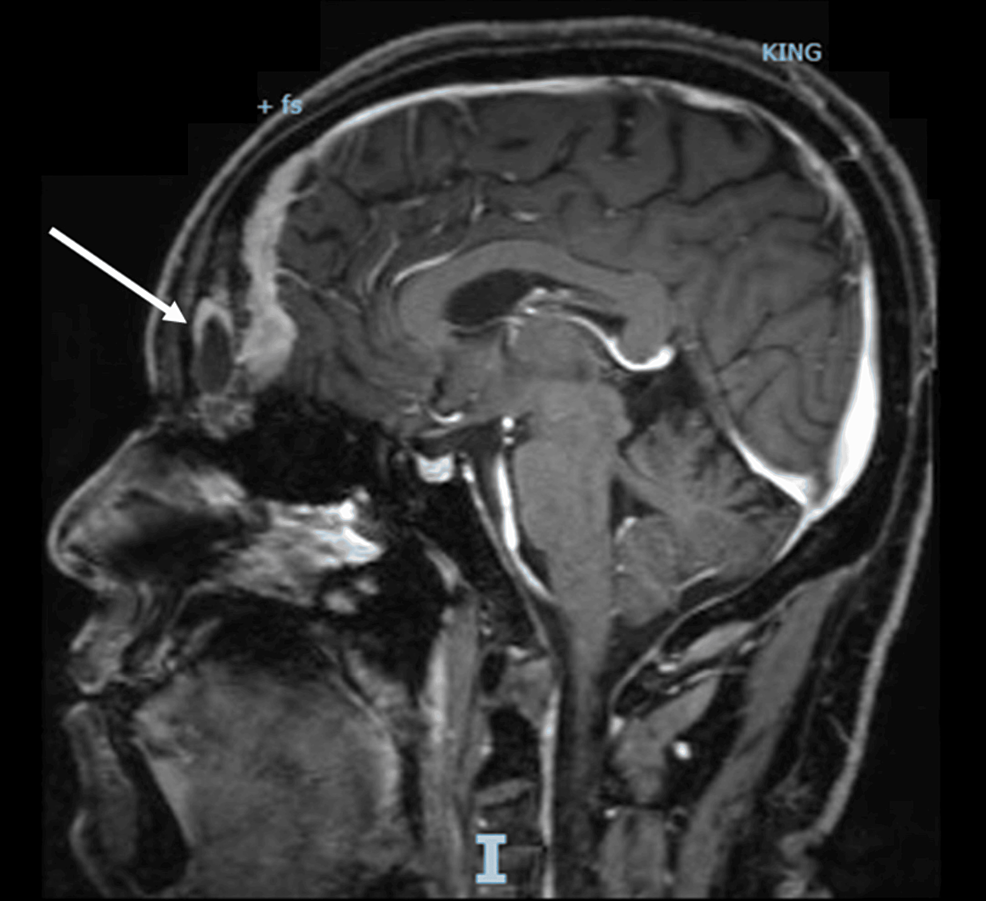
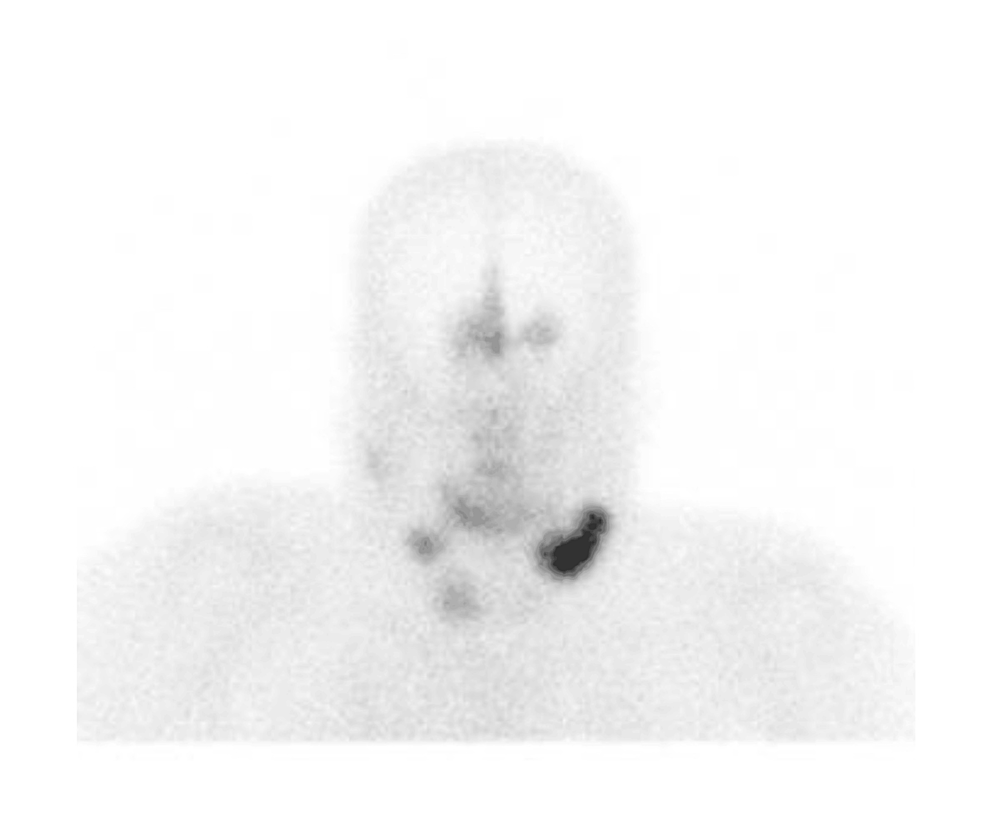
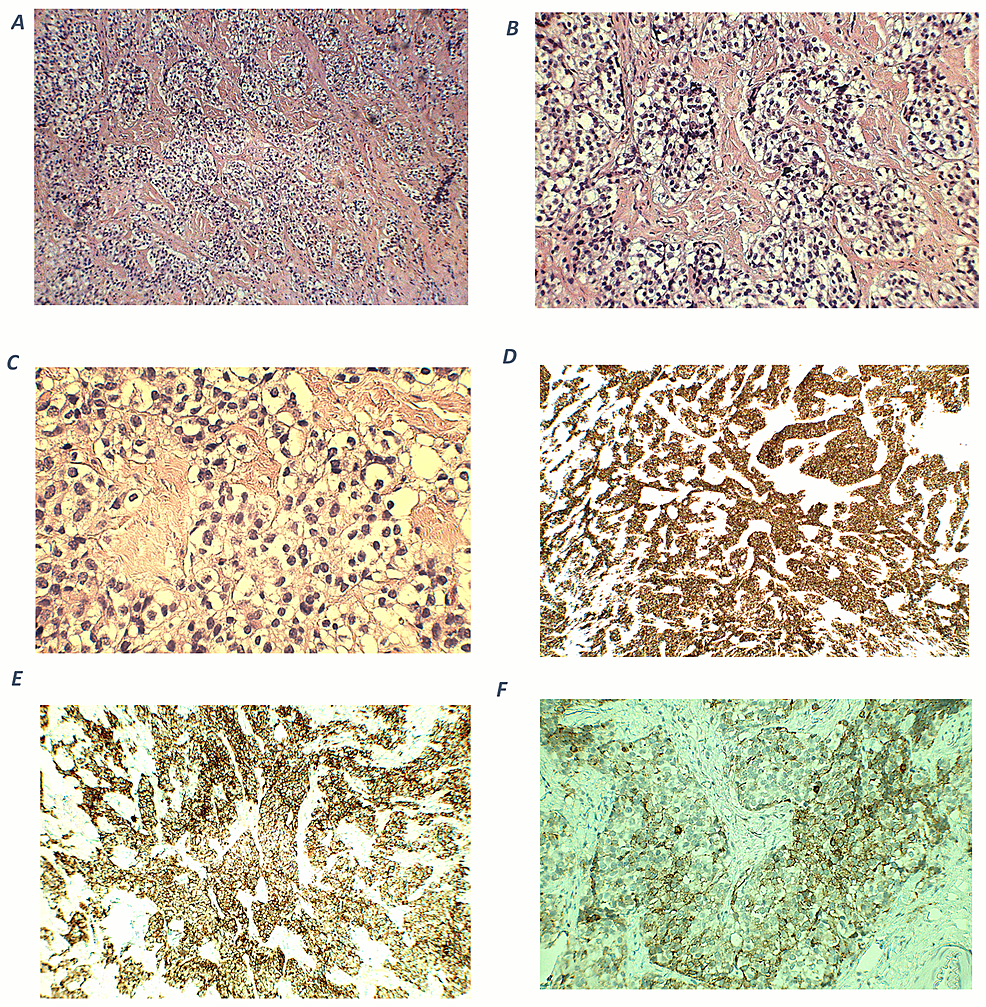
1. Acebes JJ, Martino J, Masuet C, Montanya E, Soler J : Early post-operative ACTH and cortisol as predictors of remission in Cushing’s disease.
Acta Neurochir (Wien) 149 : 471-477; discussion 477-479, 2007


2. Aranda G, Enseñat J, Mora M, Puig-Domingo M, Martínez de Osaba MJ, Casals G, et al : Long-term remission and recurrence rate in a cohort of Cushing’s disease: the need for long-term follow-up.
Pituitary 18 : 142-149, 2015


3. Araujo-Castro M, Acitores Cancela A, Vior C, Pascual-Corrales E, Rodríguez Berrocal V : Radiological Knosp, revised-Knosp, and Hardy-Wilson classifications for the prediction of surgical outcomes in the endoscopic endonasal surgery of pituitary adenomas: study of 228 cases.
Front Oncol 11 : 807040, 2022



6. Brichard C, Costa E, Fomekong E, Maiter D, Raftopoulos C : Outcome of transsphenoidal surgery for cushing disease: a single-center experience over 20 years.
World Neurosurg 119 : e106-e117, 2018


8. Cebula H, Baussart B, Villa C, Assié G, Boulin A, Foubert L, et al : Efficacy of endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery for Cushing’s disease in 230 patients with positive and negative MRI.
Acta Neurochir (Wien) 159 : 1227-1236, 2017


9. Chandler WF, Barkan AL, Hollon T, Sakharova A, Sack J, Brahma B, et al : Outcome of transsphenoidal surgery for cushing disease: a singlecenter experience over 32 years.
Neurosurgery 78 : 216-223, 2016

10. Ciric I, Zhao JC, Du H, Findling JW, Molitch ME, Weiss RE, et al : Transsphenoidal surgery for Cushing disease: experience with 136 patients.
Neurosurgery 70 : 70-80; discussion 80-81, 2012

11. Clayton RN, Raskauskiene D, Reulen RC, Jones PW : Mortality and morbidity in Cushing’s disease over 50 years in Stoke-on-Trent, UK: audit and meta-analysis of literature.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96 : 632-642, 2011


12. Dai C, Feng M, Sun B, Bao X, Yao Y, Deng K, et al : Surgical outcome of transsphenoidal surgery in Cushing’s disease: a case series of 1106 patients from a single center over 30 years.
Endocrine 75 : 219-227, 2022


13. Doglietto F, Maira G : Cushing disease and negative magnetic resonance imaging finding: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge.
World Neurosurg 77 : 445-447, 2012


15. Fang J, Xie S, Li N, Jiang Z : Postoperative complications of endoscopic versus microscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery: a meta-analysis.
J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 28 : 554-559, 2018


16. Feng M, Liu Z, Liu X, Bao X, Yao Y, Deng K, et al : Diagnosis and outcomes of 341 patients with Cushing’s disease following transsphenoid surgery: a single-center experience.
World Neurosurg 109 : e75-e80, 2018


17. Fleseriu M, Hamrahian AH, Hoffman AR, Kelly DF, Katznelson L; AACE Neuroendocrine, Pituitary Scientific Committee : American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Disease state clinical review: diagnosis of recurrence in Cushing disease.
Endocr Pract 22 : 1436-1448, 2016


18. Hakami OA, Ahmed S, Karavitaki N : Epidemiology and mortality of Cushing’s syndrome.
Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 35 : 101521, 2021


19. Hameed N, Yedinak CG, Brzana J, Gultekin SH, Coppa ND, Dogan A, et al : Remission rate after transsphenoidal surgery in patients with pathologically confirmed Cushing’s disease, the role of cortisol, ACTH assessment and immediate reoperation: a large single center experience.
Pituitary 16 : 452-458, 2013


20. Hardy J, Vezina JL : Transsphenoidal neurosurgery of intracranial neoplasm.
Adv Neurol 15 : 261-273, 1976

21. Juszczak A, Ertorer ME, Grossman A : The therapy of Cushing’s disease in adults and children: an update.
Horm Metab Res 45 : 109-117, 2013


22. Knosp E, Steiner E, Kitz K, Matula C : Pituitary adenomas with invasion of the cavernous sinus space: a magnetic resonance imaging classification compared with surgical findings.
Neurosurgery 33 : 610-617; discussion 617-618, 1993


23. Lambert JK, Goldberg L, Fayngold S, Kostadinov J, Post KD, Geer EB : Predictors of mortality and long-term outcomes in treated Cushing’s disease: a study of 346 patients.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98 : 1022-1030, 2013



24. Lüdecke DK, Flitsch J, Knappe UJ, Saeger W : Cushing’s disease: a surgical view.
J Neurooncol 54 : 151-166, 2001

25. Mamelak AN, Dowd CF, Tyrrell JB, McDonald JF, Wilson CB : Venous angiography is needed to interpret inferior petrosal sinus and cavernous sinus sampling data for lateralizing adrenocorticotropin-secreting adenomas.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81 : 475-481, 1996


26. McCance DR, McIlrath E, McNeill A, Gordon DS, Hadden DR, Kennedy L, et al : Bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling as a routine procedure in ACTH-dependent Cushing’s syndrome.
Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 30 : 157-166, 1989


27. Netea-Maier RT, van Lindert EJ, den Heijer M, van der Eerden A, Pieters GF, Sweep CG, et al : Transsphenoidal pituitary surgery via the endoscopic technique: results in 35 consecutive patients with Cushing’s disease.
Eur J Endocrinol 154 : 675-684, 2006


28. Nieman LK, Biller BM, Findling JW, Newell-Price J, Savage MO, Stewart PM, et al : The diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93 : 1526-1540, 2008



29. Oldfield EH, Doppman JL, Nieman LK, Chrousos GP, Miller DL, Katz DA, et al : Petrosal sinus sampling with and without corticotropin-releasing hormone for the differential diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome.
N Engl J Med 325 : 897-905, 1991


30. Petersenn S, Beckers A, Ferone D, van der Lely A, Bollerslev J, Boscaro M, et al : Therapy of endocrine disease: outcomes in patients with Cushing’s disease undergoing transsphenoidal surgery: systematic review assessing criteria used to define remission and recurrence.
Eur J Endocrinol 172 : R227-R239, 2015


31. Prevedello DM, Pouratian N, Sherman J, Jane JA Jr, Vance ML, Lopes MB, et al : Management of Cushing’s disease: outcome in patients with microadenoma detected on pituitary magnetic resonance imaging.
J Neurosurg 109 : 751-759, 2008


32. Salenave S, Gatta B, Pecheur S, San-Galli F, Visot A, Lasjaunias P, et al : Pituitary magnetic resonance imaging findings do not influence surgical outcome in adrenocorticotropin-secreting microadenomas.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89 : 3371-3376, 2004


33. Semple PL, Laws ER Jr : Complications in a contemporary series of patients who underwent transsphenoidal surgery for Cushing’s disease.
J Neurosurg 91 : 175-179, 1999

34. Serban AL, Del Sindaco G, Sala E, Carosi G, Indirli R, Rodari G, et al : Determinants of outcome of transsphenoidal surgery for Cushing disease in a single-centre series.
J Endocrinol Invest 43 : 631-639, 2020


36. Sun Y, Sun Q, Fan C, Shen J, Zhao W, Guo Y, et al : Diagnosis and therapy for Cushing’s disease with negative dynamic MRI finding: a singlecentre experience.
Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 76 : 868-876, 2012


38. Valderrábano P, Aller J, García-Valdecasas L, García-Uría J, Martín L, Palacios N, et al : Results of repeated transsphenoidal surgery in Cushing’s disease. Long-term follow-up.
Endocrinol Nutr 61 : 176-183, 2014


39. Wilson CB : A decade of pituitary microsurgery. The Herbert Olivecrona lecture.
J Neurosurg 61 : 814-833, 1984

40. Yamada S, Fukuhara N, Nishioka H, Takeshita A, Inoshita N, Ito J, et al : Surgical management and outcomes in patients with Cushing disease with negative pituitary magnetic resonance imaging.
World Neurosurg 77 : 525-532, 2012