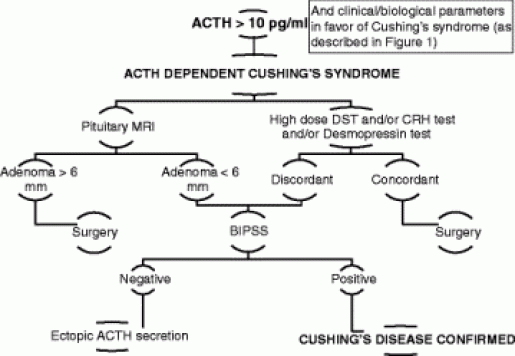
Cushing disease is caused by tumour in the pituitary gland which leads to excessive secretion of a hormone called adrenocorticotrophic (ACTH), which in turn leads to increasing levels of cortisol in the body. Cortisol is a steroid hormone released by the adrenal glands and helps the body to deal with injury or infection. Increasing levels of cortisol increases the blood sugar and can even cause diabetes mellitus. However the disease is also caused due to excess production of hypothalamus corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) which stimulates the synthesis of cortisol by the adrenal glands.
The condition is named after Harvey Cushing, the doctor who first identified the disease in 1912. Cushing disease results in Cushing syndrome. Cushing syndrome is a group of signs and symptoms developed due to prolonged exposure to cortisol.
Signs and symptoms of Cushing syndrome includes hypertension, abdominal obesity, muscle weakness, headache, fragile skin, acne, thin arms and legs, red stretch marks on stomach, fluid retention or swelling, excess body and facial hair, weight gain, acne, buffalo hump, tiredness, fatigue, brittle bones, low back pain, moon shaped face etc.
Symptoms vary from individual to individual depending upon the disease duration, age and gender of the patient. Disease diagnosis is done by measuring levels of cortisol in patient’s urine, saliva or blood. For confirming the diagnosis, a blood test for ACTH is performed. The first-line treatment of the disease is through surgical resection of ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma, however disease management is also done through medications, Cushing disease treatment market comprises of the drugs designed for lowering the level of cortisol in the body. Thus patients suffering from Cushing disease are prescribed medications such as ketoconazole, mitotane, aminoglutethimide metyrapone, mifepristone, etomidate and pasireotide.
Request to View Tables of Content @ http://www.persistencemarketresearch.com/toc/14155
Cushing’s disease treatment market revenue is growing with a stable growth rate, this is attributed to increasing number of pipeline drugs. Also increasing interest of pharmaceutical companies to develop Cushing disease drugs is a major factor contributing to the revenue growth of Cushing disease treatment market over the forecast period. Current and emerging players’ focuses on physician education and awareness regarding availability of different drugs for curing Cushing disease, thus increasing the referral speeds, time to diagnosis and volume of diagnosed Cushing disease individuals. Growing healthcare expenditure and increasing awareness regarding Cushing syndrome aids in the revenue growth of Cushing’s disease treatment market. Increasing number of new product launches also drives the market for Cushing’s disease Treatment devices. However availability of alternative therapies for curing Cushing syndrome is expected to hamper the growth of the Cushing’s disease treatment market over the forecast period.
The Cushing’s disease Treatment market is segment based on the product type, technology type and end user
Cushing’s disease Treatment market is segmented into following types:
By Drug Type
- Ketoconazole
- Mitotane
- Aminoglutethimide
- Metyrapone
- Mifepristone
- Etomidate
- Pasireotide
By End User
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Drug Stores
- Clinics
- e-Commerce/Online Pharmacies
Cushing’s disease treatment market revenue is expected to grow at a good growth rate, over the forecast period. The market is anticipated to perform well in the near future due to increasing awareness regarding the condition. Also the market is anticipated to grow with a fastest CAGR over the forecast period, attributed to increasing investment in R&D and increasing number of new product launches which is estimated to drive the revenue growth of Cushing’s disease treatment market over the forecast period.
Depending on geographic region, the Cushing’s disease treatment market is segmented into five key regions: North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC) and Middle East & Africa (MEA).
North America is occupying the largest regional market share in the global Cushing’s disease treatment market owing to the presence of more number of market players, high awareness levels regarding Cushing syndrome. Healthcare expenditure and relatively larger number of R&D exercises pertaining to drug manufacturing and marketing activities in the region. Also Europe is expected to perform well in the near future due to increasing prevalence of the condition in the region.
Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR because of increase in the number of people showing the symptoms of Cushing syndrome, thus boosting the market growth of Cushing’s disease treatment market throughout the forecast period.
Some players of Cushing’s disease Treatment market includes CORCEPT THERAPEUTICS, HRA Pharma, Strongbridge Biopharma plc, Novartis AG, etc. However there are numerous companies producing branded generics for Cushing disease. The companies in Cushing’s disease treatment market are increasingly engaged in strategic partnerships, collaborations and promotional activities to capture a greater pie of market share.
Buy Now: You can now buy a single user license of the report at http://www.persistencemarketresearch.com/checkout/14155
The final report customized as per your specific requirement will be sent to your e-mail id within 7-20 days, depending on the scope of the report.
The research report presents a comprehensive assessment of the market and contains thoughtful insights, facts, historical data, and statistically supported and industry-validated market data. It also contains projections using a suitable set of assumptions and methodologies. The research report provides analysis and information according to categories such as market segments, geographies, types, technology and applications.
For more information, please e-mail us at sales@persistencemarketresearch.com
About Us
Persistence Market Research (PMR) is a U.S.-based full-service market intelligence firm specializing in syndicated research, custom research, and consulting services. PMR boasts market research expertise across the Healthcare, Chemicals and Materials, Technology and Media, Energy and Mining, Food and Beverages, Semiconductor and Electronics, Consumer Goods, and Shipping and Transportation industries. The company draws from its multi-disciplinary capabilities and high-pedigree team of analysts to share data that precisely corresponds to clients’ business needs.
PMR stands committed to bringing more accuracy and speed to clients’ business decisions. From ready-to-purchase market research reports to customized research solutions, PMR’s engagement models are highly flexible without compromising on its deep-seated research values.
Contact
Persistence Market Research Pvt. Ltd
305 Broadway
7th Floor, New York City,
NY 10007, United States,
USA – Canada Toll Free: 800-961-0353
Email: sales@persistencemarketresearch.com
media@persistencemarketresearch.com
Web: http://www.persistencemarketresearch.com