IMPORTANT! A new study finds that the Roundup herbicide disrupts the hormonal system of rats at low levels at which it’s meant to produce no adverse effects. By the same mechanism It may be causing the potentially fatal condition of ‘adrenal insufficiency’ in humans.
Monsanto’s glyphosate-based herbicide Roundup is an endocrine (hormone) disruptor in adult male rats, a new study shows.
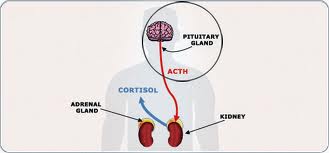
The lowest dose tested of 10 mg/kg bw/d (bodyweight per day) was found to reduce levels of corticosterone, a steroid hormone produced in the adrenal glands. This was only one manifestation of a widespread disruption of adrenal function.
No other toxic effects were seen at that dose, so if endocrine disruption were not being specifically looked for, there would be no other signs that the dose was toxic. However a 2012 study detected a 35% testosterone down-regulation in rats at a concentration of 1 part per million.
In both studies endocrine disruption was detected at the lowest level tested for, so we don’t know if, when it comes to endocrine disruption, there are ‘safe’ lower doses of Roundup. In technical parlance, this means that no NOAEL (no observed adverse effect level), was found.
Significantly, the authors believe that the hormonal disruption could lead to the potentially fatal condition know as ‘adrenal insufficiency’ in humans, which causes fatigue, anorexia, sweating, anxiety, shaking, nausea, heart palpitations and weight loss.
“A progressive increase in its prevalence has been observed in humans, while a very few studies relating to xenobiotic exposure and adrenal insufficiency development have been reported”, they write. The increasing levels of Roundup in the environment and food could be “one of the possible mechanisms of adrenal insufficiency.”
How does this level relate to safety limits set by regulators?
One problem with trying to work out how the endocrine disruptive level of 10 mg/kg bw/d relates to how ‘safe’ levels are set by regulators.
The experiment looked at Roundup, the complete herbicide formulation as sold and used, but regulators only look at the long-term safety of glyphosate alone, the supposed active ingredient of Roundup.
Safe levels for chronic exposure to the Roundup herbicide product have never been tested or assessed for regulatory processes. This is a serious omission because Roundup has been shown in many tests to be more disruptive to hormones than glyphosate alone, thanks to the numerous other ingredients it contains to enhance its weed-killing properties.
Given this yawning data gap, let’s for a moment assume that the regulatory limits set for glyphosate alone can be used as a guide for the safe level of Roundup.
The endocrine disruptive level of Roundup found in the experiment, of 10 mg/kg bw/d, is is well above the acceptable daily intake (ADI) set for glyphosate in Europe (0.3 mg/kg bw/d) and the US (1.75 mg/kg bw/d). But this isn’t a reason to feel reassured, since with endocrine effects, low doses can be more disruptive than higher doses.
Another worrying factor is that 10 mg/kg bw/d is well below the NOAEL (no observed adverse effect level) for chronic toxicity of glyphosate: 500 mg/kg bw/d for chronic toxicity, according to the US EPA.
In other words, the level of 500 mg/kg bw/d – a massive 50 times higher than the level of Roundup found to be endocrine disruptive in the experiment – is deemed by US regulators not to cause chronic toxicity.
This experiment shows they are wrong by a long shot. They failed to see toxicity below that level because they failed to take endocrine disruptive effects from low doses into account and industry does not test for them.
Hormone disruption take place at or below ‘no adverse effects’ levels
Interestingly, the NOAEL for glyphosate in industry’s three-generation reproductive studies in rats was much lower than that for chronic toxicity – 30 mg/kg bw/day for adults and 10 mg/kg bw/day for offspring.
However the latter figures – at which no adverse effects should be apparent from glyphosate – are at the same as or higher level than the level of Roundup found to be endocrine disruptive in the new study.
These results therefore show that the reproductive processes of the rats are sensitive to low doses that are apparently not overtly toxic. This in turn suggests that the reproductive toxicity findings are due to endocrine disruptive effects.
Regulatory tests still do not include tests for endocrine disruption from low doses, in spite of the fact that scientists have known about the syndrome since the 1990s.
In the final section of the new study, the researchers discuss its implications. They note that the effects seen in the Roundup-treated rats to the Adrenocorticotropic hormone receptor (ACTH) were similar to adrenal insufficiency in humans:
“The findings that Roundup treatment down regulates endogenous ACTH, is similar to the condition known as adrenal insufficiency in humans. This condition manifests as fatigue, anorexia, sweating, anxiety, shaking, nausea, heart palpitations and weight loss. Chronic adrenal insufficiency could be fatal, if untreated.
“A progressive increase in its prevalence has been observed in humans, while a very few studies relating to xenobiotic exposure and adrenal insufficiency development have been reported. The present study describes one of the possible mechanisms of adrenal insufficiency due to Roundup and suggests more systematic studies, to investigate the area further. “
Claire Robinson of GMWatch commented: “Since no safe dose has been established for Roundup with regard to endocrine disrupting effects, it should be banned.”
The study: ‘Analysis of endocrine disruption effect of Roundup in adrenal gland of male rats‘ is by Aparamita Pandey and Medhamurthy Rudraiah, and published in Toxicology Reports 2 (2015) pp.1075-1085 on open access.
This article was originally published by GMWatch. This version has been subject to some edits and additions by The Ecologist.
From http://www.theecologist.org/News/news_round_up/2985058/roundup_may_cause_potentially_fatal_adrenal_insufficiency.html
Filed under: adrenal, adrenal crisis, Rare Diseases | Tagged: adrenal insufficiency, anorexia, anxiety, corticosterone, fatigue, heart palpitations, herbicide, Hormone, nausea, Roundup, shaking, sweating, weight loss | Leave a comment »











 Radiation therapy can be effective in controlling the growth of the tumor. However, if you received radiation therapy in the past, additional radiation may not be safe.
Radiation therapy can be effective in controlling the growth of the tumor. However, if you received radiation therapy in the past, additional radiation may not be safe. Medical therapies for the treatment of Nelson’s syndrome are currently limited, but include:
Medical therapies for the treatment of Nelson’s syndrome are currently limited, but include: