By LISA SANDERS, M.D.
On Thursday we challenged Well readers to take the case of a 29-year-old woman with an injured groin, a swollen foot and other abnormalities. Many of you found it as challenging as the doctors who saw her. I asked for the right test as well as the right diagnosis. More than 200 answers were posted.
The right test was…
The dexamethasone suppression test,though I counted those of you who suggested measuring the cortisol in the urine.
The right diagnosis was…
Cushing’s disease
More than a dozen of you got the right answer or the right test, but Dr. Davin Quinn, a consultant psychiatrist at the University of New Mexico Hospital, was the first to be right on both counts. As soon as he saw that the patient’s cortisol level was increased, he thought of Cushing’s. And he had treated a young patient like this one some years ago as a second year resident.
The Diagnosis:
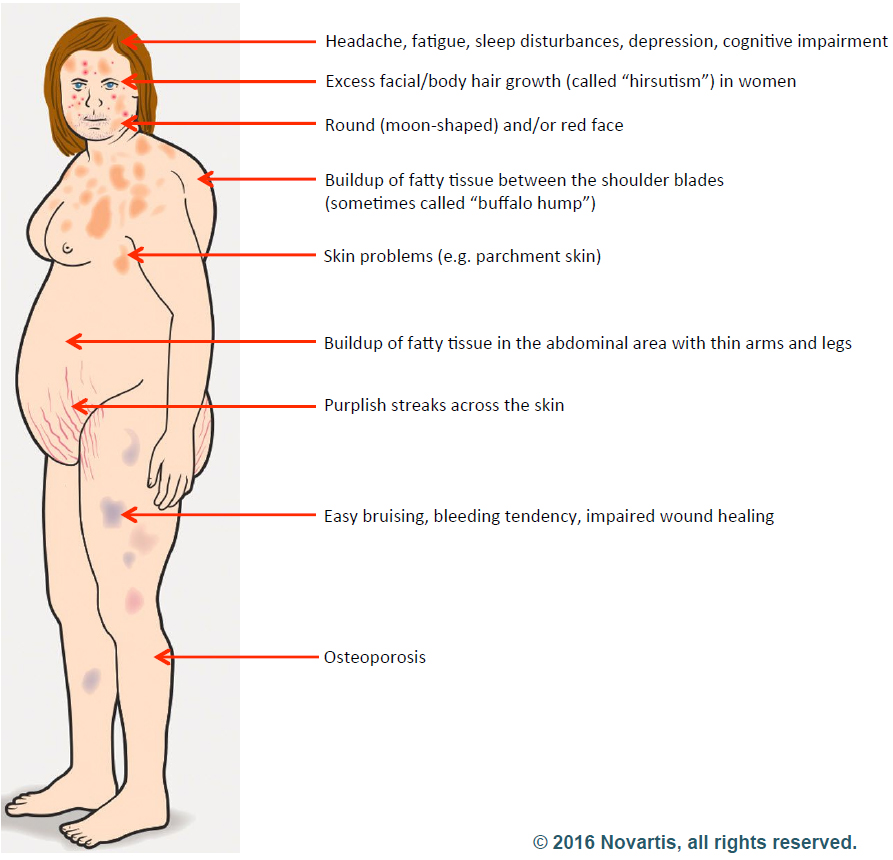
Cushing’s disease is caused by having too much of the stress hormone cortisol in the body. Cortisol is made in the adrenal glands, little pyramid shaped organs that sit atop the kidneys. It is normally a very tightly regulated hormone that helps the body respond to physical stress.
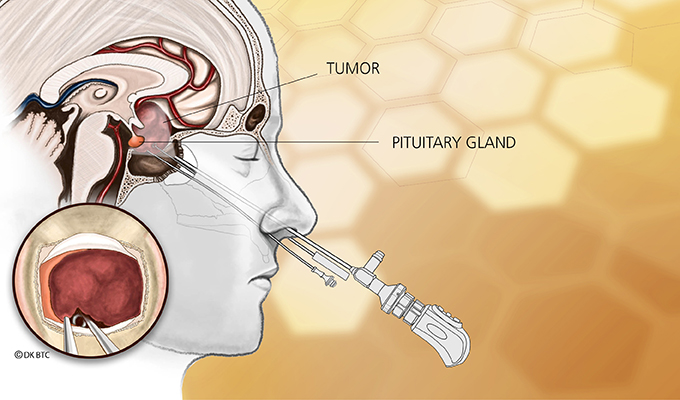
Sometimes the excess comes from a tumor in the adrenal gland itself that causes the little organ to go into overdrive, making too much cortisol. More often the excess occurs when a tumor in the pituitary gland in the brain results in too much ACTH, the hormone that controls the adrenal gland.
In the body, cortisol’s most fundamental job is to make sure we have enough glucose around to get the body’s work done. To that end, the hormone drives appetite, so that enough fuel is taken in through the food we eat. When needed, it can break muscle down into glucose. This essential function accounts for the most common symptoms of cortisol excess: hyperglycemia, weight gain and muscle wasting. However, cortisol has many functions in the body, and so an excess of the hormone can manifest itself in many different ways.
Cushing’s was first described by Dr. Harvey Cushing, a surgeon often considered the father of modern neurosurgery. In a case report in 1912, he described a 23-year-old woman with sudden weight gain, mostly in the abdomen; stretch marks from skin too thin and delicate to accommodate the excess girth; easy bruising; high blood pressure and diabetes.
Dr. Cushing’s case was, it turns out, a classic presentation of the illness. It wasn’t until 20 years later that he recognized that the disease had two forms. When it is a primary problem of an adrenal gland gone wild and producing too much cortisol on its own, the disease is known as Cushing’s syndrome. When the problem results from an overgrown part of the pituitary making too much ACTH and causing the completely normal adrenal glands to overproduce the hormone, the illness is called Cushing’s disease.
It was an important distinction, since the treatment often requires a surgical resection of the body part where the problem originates. Cushing’s syndrome can also be caused by steroid-containing medications, which are frequently used to treat certain pulmonary and autoimmune diseases.
How the Diagnosis Was Made:
After the young woman got her lab results from Dr. Becky Miller, the hematologist she had been referred to after seeing several other specialists, the patient started reading up on the abnormalities that had been found. And based on what she found on the Internet, she had an idea of what was going on with her body.
“I think I have Cushing’s disease,” the patient told her endocrinologist when she saw him again a few weeks later.
The patient laid out her argument. In Cushing’s, the body puts out too much cortisol, one of the fight-or-flight stress hormones. That would explain her high blood pressure. Just about everyone with Cushing’s disease has high blood pressure.
She had other symptoms of Cushing’s, too. She bruised easily. And she’d been waking up crazy early in the morning for the past year or so – around 4:30 – and couldn’t get back to sleep. She’d heard that too much cortisol could cause that as well. She was losing muscle mass – she used to have well-defined muscles in her thighs and calves. Not any more. Her belly – it wasn’t huge, but it was a lot bigger than it had been. Cushing’s seemed the obvious diagnosis.
The doctor was skeptical. He had seen Cushing’s before, and this patient didn’t match the typical pattern. She was the right age for Cushing’s and she had high blood pressure, but nothing else seemed to fit. She wasn’t obese. Indeed, she was tall (5- foot-10) and slim (150 pounds) and athletic looking. She didn’t have stretch marks; she didn’t have diabetes. She said she bruised easily, but the endocrinologist saw no bruises on exam. Her ankle was still swollen, and Cushing’s can do that, but so can lots of other diseases.
The blood tests that Dr. Miller ordered measuring the patient’s ACTH and cortisol levels were suggestive of the disease, but many common problems — depression, alcohol use, eating disorders — can cause the same result. Still, it was worth taking the next step: a dexamethasone suppression test.
Testing, Then Treatment:
The dexamethasone suppression test depends on a natural negative feedback loop whereby high levels of cortisol suppress further secretion of the hormone. Dexamethasone is an artificial form of cortisol. Given in high doses, it will cause the level of naturally-occurring cortisol to drop dramatically.
The patient was told to take the dexamethasone pills the night before having her blood tested. The doctor called her the next day.
“Are you sure you took the pills I gave you last night?” the endocrinologist asked her over the phone. The doctor’s voice sounded a little sharp to the young woman, tinged with a hint of accusation.
“Of course I took them,” she responded, trying to keep her voice clear of any irritation.
“Well, the results are crazy,” he told her and proposed she take another test: a 24-hour urine test.
Because cortisol is eliminated through the kidneys, collecting a full day’s urine would show how much cortisol her body was making. So the patient carefully collected a day’s worth of urine.
A few days later, the endocrinologist called again: her cortisol level was shockingly high. She was right, the doctor conceded, she really did have Cushing’s.
An M.R.I. scan revealed a tiny tumor on her pituitary. A couple of months later, she had surgery to remove the affected part of the gland.
After recovering from the surgery, the patient’s blood pressure returned to normal, as did her red blood cell count and her persistently swollen ankle. And she was able to once again sleep through the night.
Red Herrings Everywhere:
As many readers noted, there were lots of findings that didn’t really add up in this case. Was this woman’s groin sprain part of the Cushing’s? What about the lower extremity swelling, and the excess red blood cell count?
In the medical literature, there is a single case report of high red blood cell counts as the presenting symptom in a patient with Cushing’s. And with this patient, the problem resolved after her surgery – so maybe they were linked.
And what about the weird bone marrow biopsy? The gastritis? The enlarged spleen? It’s hard to say for certain if any of these problems was a result of the excess cortisol or if she just happened to have other medical problems.
Why the patient didn’t have the typical symptoms of Cushing’s is easier to explain. She was very early in the course of the disease when she got her diagnosis. Most patients are diagnosed once symptoms have become more prominent
By the time this patient had her surgery, a couple of months later, the round face and belly characteristic of cortisol excess were present. Now, two years after her surgery, none of the symptoms remain.
From http://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2014/01/17/think-like-a-doctor-red-herrings-solved/?_php=true&_type=blogs&_r=0
Filed under: adrenal, Cushing's, pituitary | Tagged: 24-hour urine free cortisol test, ACTH, adrenal, alcohol, blood pressure, bone marrow biopsy, bruising, cortisol, Cushing's Disease, Cushing's Syndrome, depression, dexamethasone suppression test, diabetes, Dr. Becky Miller, Dr. Davin Quinn, Dr. Harvey Cushing, foot, gastritis, groin, hematologist, Hormone, hyperglycemia, kidneys, MRI, muscle wasting, Neurosurgery, pituitary, psychiatrist, red blood cell, spleen, stretch marks, striae, surgery, swelling, thin skin, tumor, UFC, University of New Mexico Hospital, urine, weight | Leave a comment »